Economic Indicators Affecting Forex Markets
Now let’s take a look at
economic indicators list for FX:
- Central Bank Interest Rates
- Bond Yields
- Inflation
- Economic Growth
- Central Bank Balance Sheet
- Budget Surplus/Deficit
- Stock Market Performance
- Geopolitical Stability
- Commodity Prices
This is a rather lengthy list, however, following just one or two measures can be misleading when making trading decisions.
Let us go through the types of indicators on the FX market in-depth:
1 - Central Bank Interest Rates
We know that central banks set the key interest rate. Every country defines this slightly differently. However, essentially in all those cases, this is the rate, at which the commercial banks get their loans from the Central Bank.
The key interest rate is usually very close to the rate which the depositor gets when opening a certificate of deposit or savings account. This makes sense because why would, for example, an American banker pay a customer 5% interest when he can borrow money from the Federal Reserve at 0.25%?
It is true, that some small financial institutions might have slightly higher rates in order to attract new customers, however, the difference usually is not that large.
Not all investors put their entire capital in the stock market and real estate. Some of them prefer to keep a portion of their wealth in more liquid investments, like CDs and Savings accounts.
For example, let’s suppose that an individual is looking to invest $100,000. Banks in his home country pay only 0.25% on the savings account. At the same time, he has an option to convert his money to some other currency and get a 5% yielding account. Therefore, he or she should receive $4,750 more interest, compared to the first option.
Everything else being equal, this makes currencies with higher central bank interest rates more attractive.
2 - Bond Yields
This is another one of the high impact Forex indicators. Obviously, CDs and Savings accounts are not the only options for an investor, looking for a liquid investment. Some of them prefer government Bonds. If one country pays a higher interest rate on his treasury securities, then it makes their currency more attractive.
However, this indicator works with governments, which have similar credit rating scores.
For example, at the time of writing, the 10 years US Treasury yields 0.85%, when a 10-year treasury bond stands at 7.25%.
If Russia, like the US, had a AAA rating, then this would make Ruble very attractive; however, according to Fitch, it has BBB-, with a past history of default. Therefore the risk here is much higher and comparing those rates is not really an apple to apple comparison.
On the other hand, if some AAA rating country’s Bond yields start rising and surpass 3 or 4%, that might make the local currency more attractive.
3 - Inflation
Inflation is one of the most important long term economic indicators that impact the Forex market. Basically it is the rate, at which the given currency loses the purchasing power. The historical average inflation in the US is 3%.
As for the latest date, according to the US Bureau of Labor and Statistics, currently, the consumer price index stands at 2.3%. This means that the consumer needs $102.30 to afford the same basket goods and services, as $100 bought a year ago.
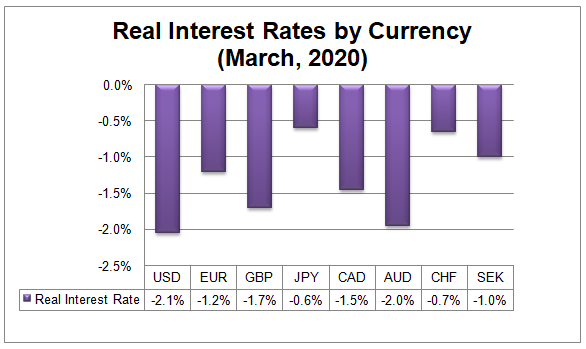
In order to get a more accurate picture of the FX market, it is useful to subtract the inflation rate from the key central bank interest rate. Let’s take the upper band of the Federal Funds rate range, which is 0.25%. So some depositors might get a return, close to that number, but at the same time, their savings might lose 2.3% of their purchasing power.
Therefore the real interest rate in the US stands at -2.05%. In Japan, the central bank rate is even lower at -0.1%. However, taking into account the current 0.5% annual inflation in the country, it puts the real interest rates in Japan at -0.6%.
Subsequently, everything else being equal this should be positive for JPY, especially when considering the USD/JPY pair.
In the long term, the relative real exchange rates might be among the economic indicators with the highest impact on FX.
4 - Economic Growth
When discussing indicators to follow in the Forex market, the economic growth comes up as one of the measures to which the financial media pays most of the attention.
This is quite logical since the persistently weak and low economic growth does create an expectation that the central bank will resort to lowering interest rates and even start QE.
On the other hand, a sustained high level of GDP growth does have the potential to increase the expected rate of return from money market accounts, real estate investments and stock dividends. This makes the currency more attractive to potential investors.
Also, it is useful to take into consideration both sides of the currency pair. When analyzing this, one country’s economy might be doing well, but at the same time, the other currency might still appreciate, because of even better economic performance.
5 - Central Bank Balance Sheet
The size of the Central Bank balance sheet is one of the economic indicators worth following in the Forex market. Here is where the basic economic principle of supply and demand comes into play.
The aggressive expansion of the balance sheet does not only eventually increase the money in circulation, but as the previous experience of 2008 aftermath has shown us, this also has an effect of suppressing returns across the range of investments.
Why is this the case? Well, faced with near 0% interest rates, parking savings on 0.1% might not make much sense.
Instead, taking advantage of the low interest rates many investors move on to real estate. Some of them find a better alternative in the stock markets. After some time the market becomes crowded, which pushes the dividend and rental yields much lower.
It goes without saying that this process makes the currency in question far less appealing compared to its counterparts.
6 - Budget Surplus/Deficit
This is another one of those useful economic indicators on the Forex market. Actually, there are both short term and long term considerations. Over a small-time horizon, the increasing budget deficit with a spending stimulus can push the yields higher, so this can benefit the currency.
However, in the long term reducing the budget deficit can be beneficial for the country’s economy and subsequently to its currency.
To illustrate this, let’s take a look at the performance of USD from 1996-2001. From 1993 the US government started to tackle the budget deficit and reduced it significantly. By 1998, the country ran a budget surplus for the first time in decades.
During the early 90s, this policy did not have a much visible positive effect on the dollar's strength; however, from 1996 the USD started to appreciate significantly against its main rivals. By 2001, the EUR/USD fell to as low as 0.85.
Clearly, there were other factors in play as well; however, this was one of the indicators, which benefited USD by that time.
7 - Stock Market Performance
As mentioned before, the
GDP growth rate can be one of the important economic indicators in the Forex market. However, this has one major downside: it is reported after the fact. So if there was a recession, this will be reported 3 or 6 months after the fact in GDP report; By that time this downturn might be already priced in FX and it might be too late to make timely trading and investment decisions.
This is where the stock market indices can be handy. They do fluctuate greatly on daily bases, however, a sustained and significant decline in the stock prices can be an early warning sign of recession, before official statistical data could confirm it.
8 - Geopolitical Stability
The market data measures are not the only reliable economic indicators for FX. The major geopolitical events can have a huge impact on currency movements.
In times of global turmoil and crisis, people usually favor safe heavens and liquidity, both of which very often benefit the USD.
The recent performance of GBP/USD is one example of this. At the beginning of March 2020, the pair stood around 1.30, however as the coronavirus crisis worsened, in two weeks it collapsed below 1.15. This kind of sharp movement in such a short time frame is rather rare in FX markets; however, in times of emergency, people are more concerned with safety rather than higher returns.
Under normal circumstances, investors might risk investing in emerging market currencies, in order to achieve higher returns than in developing countries. However, in times of crisis, the fear of losing the principal becomes a dominant factor. As a result, most investors decide to liquidate those investments for the safety of US treasuries or Bank CDs.
9 - Commodity Prices
The price of oil and gold can be helpful economic indicators for Forex trading. The commodity prices have the highest impact on USD/CAD, RUB/USD and to currencies, linked to oil production.
The recent collapse of Ruble is just one example. At the time of writing, the WTI Crude fell from $50 a month ago to $23. This is a serious blow to the Russian economy since the income from the oil sector represents half of all of its budget revenue. As a result, the ruble fell sharply during the last couple of weeks.
Following the performance of USD can be helpful for forecasting a gold price. Strong USD sometimes suppresses the prices of precious metals.
Returning to our earlier example, during the strong dollar period of 1999-2001, the gold price fell and mostly stayed within $250-$300, which is incredibly low level, especially considering the current prices.