Forecasting the Forex Market
Let us go through those factors which can help with Forex predictions in more detail.
We will be talking about
- Interest Rate Decisions
- Policy Statements
- Economic Data
- Trader Sentiment
- Relative Real Interest Rates
- Fiscal Policy
- Purchasing Power Parity
Interest Rate Decisions
One of the most volatile times in the Forex Market is the days with central bank rate decisions. In general, everything else being equal, the higher-yielding currencies are more attractive for the market, then the ones with low-interest rates.
Therefore, when the central banks raise the rates, in most cases, the currency it issues, will appreciate. However, the market always tries to guess the outcome beforehand. Very often, the currency starts to make gains months before the actual rate hike.
So, then how can we work with this Forex market indicator? Nowadays nearly every central bank has it’s stated mandate. For example, the ECB targets inflation below, but close to 2%.
The US Federal Reserve has similar goals, but there are two key differences. Firstly, FED no longer uses CPI as a measuring rod for inflation, but the alternative Personal Consumption Expenditure Price Index. There are some differences in the composition of those two indicators, but in most cases, the PCEPI shows a slightly lower level of price rises, than traditional CPI.
Another difference between the policies of those two central banks is that FED is also targeting 5% unemployment, so in effect, it has a double mandate. This has significant policy implications.
For example, 2011 was an inflationary year for most countries, Both in the US and the Eurozone, the CPI indicators have exceeded 3%, well above the intended target. The ECB responded by increasing the interest rate two times, from 1% to 1.5%.
At the same time, the FED has maintained the unchanged policy, because the unemployment level was still high.
Therefore, falling inflation and the rising number of joblessness might be followed by Federal Reserve cutting rates and even starting QE. On the other hand, stronger economic performance and increasing PCEPI well above 2% can lead to rate hikes.
Policy Statements
Statements by the chairmen of major central banks can have a serious influence on Forex. Investors and other market participants are looking for hints of future policy. So listening to those press conferences can be helpful in making live Forex market forecasts.
The minutes of monetary policy meetings are also highly sought after by traders. Here they can analyze the sentiment of committee board members and find some potential clues of future policy.
Sometimes the verbal intervention might be enough to calm the markets and restore stability. For example, after the collapse of the 1.20 floor for EUR/CHF, set by the Swiss National bank, the Danish Krone came under pressure to appreciate. The Danish central bank kept EUR/DKK at a very tight range around 7.45 for decades.
Facing the threat of Swiss-style sharp currency appreciation of Krone, the officials announced that there would be ‘unlimited’ intervention to maintain the band. Most traders decided not to pick a fight with the Danish National Bank. As a result, the Krone stabilized and the narrow peg of EUR/DKK is still maintained to this day.
Economic Data
Analyzing the regular Economic data releases, such as
GDP, unemployment, CPI can be another useful tool for Forex trading forecasts. Those indicators matter in the sense that they create expectations for traders.
For example, one country’s GDP growth might be very weak with rising unemployment and near-zero inflation rate. In this case, the market participants may assume that eventually, the local central bank will resort to lowering interest rates to help the struggling economy. Consequently, they will start opening short positions for this currency.
Therefore, there is a competition in the Forex market among traders, regarding who can make accurate forecasts as early as possible and capitalize on those trades.
Trader Sentiment
There is no need to have Forex market forecast software to check this indicator. Nowadays many platforms provide us with the information of Trader Sentiment for each pair. This measure is very simple. It shows what percentage of market participants have long and short positions on that currency pair in question.
If the balance between buyers and sellers is close to 50/50, then it is difficult to come up with any conclusions. However, if this indicator turns to more extreme levels, like 80/20 or 90/10, then this shows, that the currency becomes overbought or oversold. There are very few traders remaining to keep pushing the trend. Therefore, very often such extreme levels can be a sign of major reversal.
When it comes to the major currency pairs, the trends may last for weeks. However, eventually, there is the stage of profit-taking and reversal. Consequently, trader sentiment might be a handy indicator to look for the signs of possible trend changes.
Relative Real Interest Rates
Nobody likes to lose money, being that in nominal or real terms. Investors are no exception to this. This is when the real interest rates come into play. But how can you do the Forex forecast by this method?
To answer this question, let’s take $1,000 as an example. As things currently stand, since March of 2020, the Federal Reserve has been keeping the main rate between 0 to 0.25%. Top wall street Banks do not pay as much, but it is possible to get a 0.25% savings account with some regional and online institutions.
At that rate, by the end of the year, that $1,000 can earn an extra $2.5, bringing the balance at $1,002.50. Can this sum afford at least the same number of goods and services as a $1,000 did a year ago?
Well, not really. The latest CPI report shows 2.3% inflation over the last 12 months. Even taking into account the earned interest, the real buying power of this deposit will drop to $977. This means that assuming the same CPI level, $1,002.50 will buy the same amount of goods and services as $980 did a year ago. So instead of earning some money, in real terms, the deposit has lost $20.
This might not make much difference in the short term. However, if this state of affairs persists for a long time, then this could put pressure on USD to depreciate. It is likely that investors will start looking for alternative currencies to maintain their purchasing power.
Fiscal Policy
As the annual US budget deficit surpassed $1 trillion, the opinion on the effects on fiscal policy is very much divided. Some people at financial media dismiss this as new normal, with no serious long term consequences. At the same time, such financial experts as Peter Schiff and Axel Merk do discuss the possibility of the upcoming debt crisis.
So can the Forex market be analyzed by the fiscal policy? Since 2002 EUR started a multi-year trend of appreciation. At one point in 2008, the single currency reached $1.60. However, as the debt crisis started to unfold in Greece, Italy, and some other states the EUR/USD became much more volatile..
From 2014 the pair collapsed to near parity levels. Nowadays the Eurozone countries resolved most of those issues, with Greece returning to the bond market, however, Euro undervaluation has persisted for years, currently trading near $1.12.
Obviously, such developed economies as the USA and Japan have outstanding credit ratings and more unified and efficient mechanisms in place to address those types of problems. However, if this disbalance is left unaddressed for many years, then the bond yields might rise and the governments can be forced to commit to painful cuts, tolerate higher inflation or combination of both. This can put a heavy pressure on USD and JPY to depreciate.
We had quite the opposite scenario during 1998-2001 when the US run a budget surplus for four consecutive fiscal years. By that time, the dollar index reached multi-year highs and EUR/USD fell well below 0.85.
Therefore, the budget policy can have a significant long term impact on the Forex movement.
Purchasing Power Parity
Some long term currency trends simply can not be explained by the interest rate differentials or fiscal policy decisions. One useful example of this would be USD/JPY. At the beginning of the height of dollar strength in 2001, the pair traded above ¥140. However, from the next year, a significant downtrend developed, with USD/JPY falling below ¥80 by 2011.
As the bank of Japan introduced more aggressive easing measures, the dollar regained some ground, but even nowadays the pair struggles to stay above ¥105 level.
So how can we explain this? How how to predict Forex movement in this case? Since the middle of the 90s, the Bank of Japan has maintained a near-zero rate policy, recently dropping into -0.1%. Debt to GDP ratio in this country is even higher than in the US and there is no indication of any possible policy change. JPY has long become a trader’s favorite funding currency.
Then what is the reason behind the long term decline of USD/JPY? We might find the answer in another long term factor:
Purchasing Power Parity.
The theory behind these states, that in the long term the exchange rates are influenced by the relative price levels. For example, as mentioned before the latest release puts US inflation at 2.3%. At the same time, the statistical data shows that Japanese inflations stand at 0.6%. So there is a 1.7% differential between those two countries. If this difference persists, then PPP, the exchange rate at which the relative prices of goods and services are equalized, will shift.
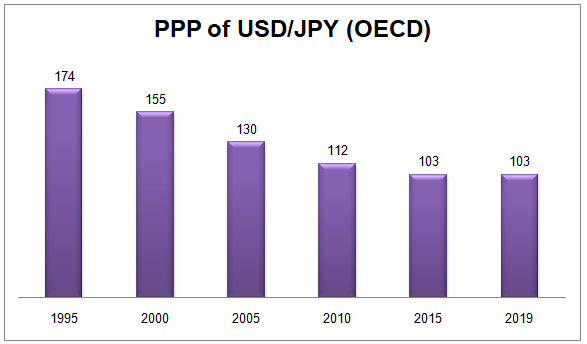
This is essentially what has been going on for the last 25 years. For decades, the Japanese Economy had experienced cycles of deflation and very low inflation. At the same time, US CPI mostly fluctuated from 2 to 3%. Because this trend lasted for many years, the PPP started to shift in USD/JPY in favor of Yen.
As we can see from this chart, according to OECD, back in 1995, ¥174 per dollar, was the rate at which the relative price of the basket of goods and services could be equalized between the two countries. Over the years the balance shifted significantly, with by 2019 PPP standing at ¥103 per dollar. This is just one example of how to analyze the Forex market trend using the Purchasing Power Parity Forex forecast indicator.